The basic material for XLPE is polyethylene, which is chemically transformed to cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) through the cross-link reaction of organic peroxides. The cross-link method for polyethylene was developed in the United States during the 1950’s and has since been continuously developed for application to higher voltages. Higher voltages are increasingly being required, and the 500kV XLPE cables have already been commercialized.
Conductor types
At present, copper (Cu) and aluminum (Al) are the main materials for XLPE conductors.
(1) Copper (Cu)
Copper (Cu) conductors have advanced electrical features, processability and economic efficiency. Therefore, they are used for the majority of underground conductor materials. Significantly, the purity of electrolytic copper needs to be 99.96%~99.86%.
(2) Aluminum (Al)
As aluminum is about one-third lighter than copper it enables easier handling. Its electrical conductivity is about two-thirds of copper but it is more economical. Because of these features, Al is the most widely used material following copper.
Benefits of XLPE
Plastic insulation is widely used in advanced nations due to its outstanding insulation, easy routing, connectivity and maintenance. Thanks to the development in cross-link technology, XLPE insulation cables can be applied to higher voltages. Recently, XLPE cables have been completely replacing OF cables. The benefits of XLPE are its lightweight, thermal characteristics, low routing costs and low material costs.
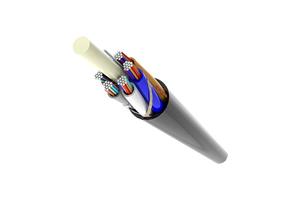
Functions and types of metal screened cables
The main objective of screening in energy cables is to shield the electric current. Other functions include safety by earthing, return conductor for fault currents in the case of ground relay or phase faults, and impact and chemical protection for armored cables.
Types of metal screened cables
Tape screening ② Wire screening ③ Aluminum screening